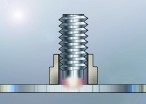
There are three types of stud welding processes: Capacitor Discharge (CD), Short Cycle (SC) and Drawn Arc (DA).

Each of these Stud Welding Processes are complementary and should not be regarded as alternatives. Typically in a production line you would chose the correct process based on your design needs.

With each method, a weld stud is held in a hand tool or production head, it is then presented squarely to the work piece and a weld occurs without breaking through the material.
With the Capacitor Discharge Process energy is stored in a bank of capacitors, which are charged to a pre-set voltage, determined by the type and size of stud and the parent material. When triggered...
View CD Process
A transformer rectifier supplies a fixed current power source, triggering produces a pilot arc and the stud lifts to a pre-set height.The main arc melts the end of the stud, producing...
View SC Process
With this process, the current level and weld duration are determined by the stud diameter. Triggering produces a pilot arc and the stud lifts to a preset height. The main arc melts the end of the stud, producing a molten...
View DA Process